Abstract
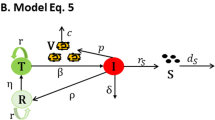
We formulate and analyze a within-host hepatitis B viral mathematical model for hepatitis B in the acute phase of infection. The model incorporates hepatocytes, hepatitis B virus, immune system cells and cytokine dynamics using a system of ordinary differential equations. We use the model to demonstrate the trends of the hepatitis B infection qualitatively without the effects of immune cells and cytokines. Using these trends, we tested the effects of incorporating the immune cells only and immune cells with cytokine responses at low and high inhibitions on the hepatitis B virus infection. Our results showed that it is impossible to have the immune cells work independently from cytokines when there is an acute hepatitis B virus infection. Therefore, our results suggest that incorporating immune cells and cytokine dynamics in the acute hepatitis B virus infection stage delays infection in the hepatocytes and excluding such dynamics speeds up infection during this phase. Results from this study are useful in developing strategies for control of hepatocellular carcinoma which is caused by hepatitis B virus infection.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed R, Gray D (1996) Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science 272(5258):54
Bauer AL, Hogue IB, Marino S, Krischner DE (2008) The effects of HIV-1 infection on latent tuberculosis. Math Model Nat Phenom 3(7):229–266
Berger A (2000) Th1 and Th2 responses: what are they? Br Med J 321(7258):424
Bility MT, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Luan Y, Li F, Chi L, Zhang L, Tu Z, Gao Y, Fu Y et al (2014) Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and m2-like macrophages. PLoS Pathog 10(3):e1004032
Budhu A, Wang XW (2006) The role of cytokines in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Leukoc Biol 80(6):1197–1213
Chang K-M, Chisari FV (1999) Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Liver Dis 3(2):221–239
Ciupe SM, Ribeiro RM, Nelson PW, Dusheiko G, Perelson AS (2007a) The role of cells refractory to productive infection in acute hepatitis B viral dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(12):5050–5055
Ciupe SM, Ribeiro RM, Nelson PW, Perelson AS (2007b) Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Theor Biol 247(1):23–35
Culshaw RV, Ruan S (2000) A delay-differential equation model of hiv infection of CD4+ T-cells. Math Biosci 165(1):27–39
Day J, Friedman A, Schlesinger LS (2009) Modeling the immune rheostat of macrophages in the lung in response to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(27):11246–11251
Eikenberry S, Hews S, Nagy JD, Kuang Y (2009) The dynamics of a delay model of HBV infection with logistic hepatocyte growth. Math Biosci Eng 6:283–299
Elenkov IJ, Chrousos GP (2002) Stress hormones, proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, and autoimmunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 966(1):290–303
Fausto N (2004) Liver regeneration and repair: hepatocytes, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Hepatology 39(6):1477–1487
Friedman A, Hao W (2017) Mathematical modeling of liver fibrosis. Math Biosci Eng 14(1):143–164
Friedman A, Siewe N (2018) Chronic hepatitis b virus and liver fibrosis: a mathematical model. PloS One 13(4):e0195037
Friedman A, Turner J, Szomolay B (2008) A model on the influence of age on immunity to infection with mycobacterium tuberculosis. Exp Gerontol 43(4):275–285
Gonzalez MDM (2017) Hepatitis B virus. Antimicrobe at http://www.antimicrobe.org/v22.asp
Guiot C, Delsanto PP, Carpinteri A, Pugno N, Mansury Y, Deisboeck TS (2006) The dynamic evolution of the power exponent in a universal growth model of tumors. J Theor Biol 240(3):459–463
Hews S, Eikenberry S, Nagy JD, Kuang Y (2010) Rich dynamics of a hepatitis B viral infection model with logistic hepatocyte growth. J Math Biol 60(4):573–590
Hickman S, Chan J, Salgame P (2002) Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces differential cytokine production from dendritic cells and macrophages with divergent effects on naive t cell polarization. J Immunol 168(9):4636–42
Ishikawa T (2012) Immunoregulation of hepatitis b virus infection—rationale and clinical application. Nagoya J Med Sci 74(3–4):217
Ito H, Seishima M (2010) Regulation of the induction and function of cytotoxict lymphocytes by natural killer t cell. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/641757
Kimura J, Takada H, Nomura A, Ohno T, Mizuno Y, Saito M, Kusuhara K, Hara T (2004) Th1 and th2 cytokine production is suppressed at the level of transcriptional regulation in Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp Immunol 137(2):444–449
Kogan Y, Agur Z, Elishmereni M (2013) A mathematical model for the immunotherapeutic control of the th1/th2 imbalance in melanoma. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Ser B 18(4):1017–1030
Krassimira A, Carsten G, Marc B, Hans-Gert H, Michael O, Michael W (2005) Large-scale isolation of human hepatocytes for therapeutic application. Cell Transplant 14(1):845–853
Kwun HJ, Jang KL (2004) Natural variants of hepatitis b virus x protein have differential effects on the expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 32(7):2202–2213
Lee WM (1997) Hepatitis B virus infection. New Engl J Med 337(24):1733–1745
Linda JA (2007) An introduction to mathematical biology. Pearson Education Ltd, London
Longo D, Fauci A, Kasper D, Hauser S, Jameson J, Loscalzo J (2012) Harrisons manual of medicine. McGraw Hill Professional, New York City
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY et al (2013) Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 380(9859):2095–2128
Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B (2012) Cd4+ t cells: differentiation and functions. Clin Dev Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/925135
Marino S, Hogue IB, Ray CJ, Kirschner DE (2008) A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J Theor Biol 254(1):178–196
Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC (1997) Liver regeneration. Science 276(5309):60–66
Min L, Su Y, Kuang Y et al (2008) Mathematical analysis of a basic virus infection model with application to HBV infection. J Math 38(5):1573–1585
Mugwagwa T (2005) Mathematical models of coreceptor usage and a dendritic cell-based vaccine during HIV-1 infection. Ph.D. thesis, University of Cape Town
Nigade PM, Patil SL, Shinde PR (2011) Bioartificial liver bridge to liver transplantation. Immunology 2(2):77–85
Nowak MA, Bonhoeffer S, Hill AM, Boehme R, Thomas HC, McDade H (1996) Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93(9):4398–4402
O’Byrne KJ, Dalgleish AG (2001) Chronic immune activation and inflammation as the cause of malignancy. Br J Cancer 85(4):473
Organization (WHO) (2002) Hepatitis B
Perelson AS, Kirschner DE, De Boer R (1993) Dynamics of HIV infection of CD4+ T cells. Math Biosci 114(1):81–125
Phillips S, Chokshi S, Riva A, Evans A, Williams R, Naoumov NV (2010) CD8+ T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J Immunol 184(1):287–295
Ramadori G, Armbrust T (2001) Cytokines in the liver. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(7):777–784
Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT (1986) Cancer immunotherapy using interleukin-2 and interleukin-2-activated lymphocytes. Ann Rev Immunol 4(1):681–709
Sachdeva M, Chawla YK, Arora SK (2015) Immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 7(17):2080
Schuch A, Hoh A, Thimme R (2014) The role of natural killer cells and cd8 (+) T cells in hepatitis B virus infection. Front Immunol 5(258.10):3389
Seeger C, Mason WS (2000) Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(1):51–68
Thieme RH (2003) Mathematics in population biology. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Van den Driessche P, Watmough J (2002) Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math Biosci 180(1):29–48
van den Ham H-J, de Boer RJ (2008) From the two-dimensional th1 and th2 phenotypes to high-dimensional models for gene regulation. Int Immunol 20(10):1269–1277
Webster GJ, Reignat S, Maini MK, Whalley SA, Ogg GS, King A, Brown D, Amlot PL, Williams R, Vergani D et al (2000) Incubation phase of acute hepatitis B in man: dynamic of cellular immune mechanisms. Hepatology 32(5):1117–1124
Wu B-K, Li C-C, Chen H-J, Chang J-L, Jeng K-S, Chou C-K, Hsu M-T, Tsai T-F (2006) Blocking of g1/s transition and cell death in the regenerating liver of hepatitis B virus x protein transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340(3):916–928
Yates A, Callard R, Stark J (2004) Combining cytokine signalling with t-bet and gata-3 regulation in th1 and th2 differentiation: a model for cellular decision-making. J Theor Biol 231(2):181–196
Youngblood B, Hale JS, Ahmed R (2013) T-cell memory differentiation: insights from transcriptional signatures and epigenetics. Immunology 139(3):277–284
Zhang J-M, An J (2007) Cytokines, inflammation and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin 45(2):27
Zhang N, Bevan MJ (2011) CD8+ T cells: foot soldiers of the immune system. Immunity 35(2):161–168
Acknowledgements
The support of the DST-NRF Centre of Excellence in Mathematical and Statistical Sciences (CoE-MaSS) (Grant No. BA2018/008) and the University of KwaZulu-Natal, School of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, Pietermaritzburg Campus, toward this research is hereby acknowledged. Opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at are those of the author and are not necessarily to be attributed to the CoE-MaSS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manda, E.C., Chirove, F. Acute hepatitis B virus infection model within the host incorporating immune cells and cytokine responses. Theory Biosci. 139, 153–169 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-019-00305-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-019-00305-2