| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 14:17:50 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:15 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002369 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 9-cis-Retinoic acid |
|---|
| Description | 9-cis-Retinoic acid is an active retinoid that regulates expression of retinoid responsive genes, serving as a ligand for two classes of ligand-dependent transcription factors: the retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors. Retinoids (vitamin A and its analogs) are essential dietary substances that are needed by mammals for reproduction, normal embryogenesis, growth, vision, and maintaining normal cellular differentiation and the integrity of the immune system. Within cells, retinoids regulate gene transcription acting through ligand-dependent transcription factors, the retinoic acid receptors (RARs), and the retinoid X receptors (RXRs). all-trans-Retinoic acid binds only to RARs with high affinity, whereas its 9-cis isomer binds with high affinity to both RARs and RXRs. The actions of all-trans- and 9-cis-retinoic acid in regulating cellular responses are distinct and not interchangeable (PMID: 9115228 ). |
|---|
| Structure | C\C(\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=C\C(\C)=C\C(O)=O InChI=1S/C20H28O2/c1-15(8-6-9-16(2)14-19(21)22)11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-20(18,4)5/h6,8-9,11-12,14H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,21,22)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8-,16-14+ |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid | ChEBI | | (7E,9Z,11E,13E)-Retinoic acid | ChEBI | | 9(Z)-Retinoic acid | ChEBI | | 9-cis-Tretinoin | ChEBI | | Alitretinoin | ChEBI | | Alitretinoina | ChEBI | | Alitretinoine | ChEBI | | Alitretinoinum | ChEBI | | Panretin | ChEBI | | Panretyn | ChEBI | | (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoate | Generator | | (7E,9Z,11E,13E)-Retinoate | Generator | | 9(Z)-Retinoate | Generator | | 9-cis-Retinoate | Generator | | 9 cis Retinoic acid | MeSH | | 9CRA compound | MeSH | | Toctino | MeSH | | 15-apo-beta-Caroten-15-Oate | HMDB | | 15-apo-beta-Caroten-15-Oic acid | HMDB | | 9-Retinoate | HMDB | | 9-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | Aberel | HMDB | | Aberela | HMDB | | Airol | HMDB | | Aknoten | HMDB | | all-trans- Vitamin a1 acid | HMDB | | all-trans-b-Retinoate | HMDB | | all-trans-b-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | all-trans-beta-Retinoate | HMDB | | all-trans-beta-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | all-trans-Vitamin a acid | HMDB | | alpha-Vitaminsyre | HMDB | | Atragen | HMDB | | Avita | HMDB | | Avitoin | HMDB | | b-Retinoate | HMDB | | b-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | beta-Retinoate | HMDB | | beta-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | Dermairol | HMDB | | Effederm | HMDB | | Epi-aberel | HMDB | | Eudyna | HMDB | | Isotretinoin retinoate | HMDB | | Isotretinoin retinoic acid | HMDB | | Panretin gel | HMDB | | Panrexin | HMDB | | Renova | HMDB | | Retacnyl | HMDB | | Retin a | HMDB | | Retin-a | HMDB | | Retin-a micro | HMDB | | Retinoate | HMDB | | Retinoic acid | HMDB | | Retinova | HMDB | | trans-Retinoate | HMDB | | trans-Retinoic acid | HMDB | | trans-Vitamin a acid | HMDB | | Tretinoin | HMDB | | Tretinoin/all-trans retinoate | HMDB | | Tretinoin/all-trans retinoic acid | HMDB | | Tretinon | HMDB | | Vesanoid | HMDB | | Vesnaroid | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H28O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 300.4351 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 300.20893014 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4E,6Z,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | alitretinoin |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 5300-03-8 |
|---|
| SMILES | C\C(\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C)=C\C=C\C(\C)=C\C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H28O2/c1-15(8-6-9-16(2)14-19(21)22)11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-20(18,4)5/h6,8-9,11-12,14H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,21,22)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8-,16-14+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | SHGAZHPCJJPHSC-ZVCIMWCZSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Retinoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Retinoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Retinoic acid
- Diterpenoid
- Retinoid skeleton
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Branched fatty acid
- Methyl-branched fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections| Adduct Type | Data Source | CCS Value (Å2) | Reference |
|---|
| [M-H]- | MetCCS_train_neg | 200.006 | 30932474 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-000i-2190000000-86aaab132a5b092ebf10 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-5139000000-29caedb85908ca2b99f4 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0uei-0494000000-28e6366fdd47e8ba2117 | 2016-06-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052r-2980000000-3e7fc78de83c23830416 | 2016-06-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052r-5900000000-ef4d86f8bcf86959f794 | 2016-06-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052b-0090000000-e07ffb4c1e5c63ab1b59 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052b-0090000000-a0a8411213bbd2543243 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-3690000000-97e6a74798dd69c30ad1 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052b-0090000000-5f942e3b870e7bd0121b | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0190000000-22b445382d3977280045 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-016r-4900000000-0005b37f6d54a42a84f6 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0zir-0973000000-3040e9e4a1a5448efbcb | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-060c-1950000000-f3b9c9b378f60b8c49a9 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 9-cis-Retinoic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0ar3-5910000000-de22eb65f274483f3f98 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
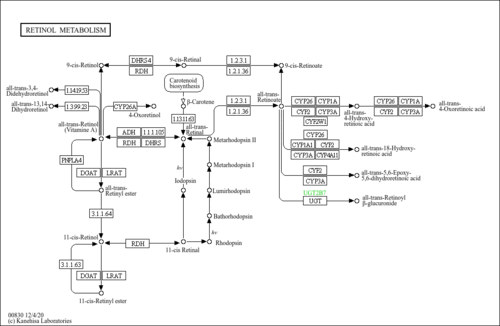
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0042 +/-0.001 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0056 +/- 0.002 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00523 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB001084 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 395778 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C15493 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Alitretinoin |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 449171 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 50648 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | Not Available |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Mertz JR, Shang E, Piantedosi R, Wei S, Wolgemuth DJ, Blaner WS: Identification and characterization of a stereospecific human enzyme that catalyzes 9-cis-retinol oxidation. A possible role in 9-cis-retinoic acid formation. J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):11744-9. [PubMed:9115228 ]
|
|---|