Abstract
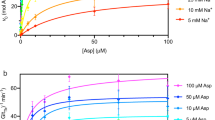
This study investigates the reverse mode of the Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). In giant excised inside-out membrane patches from Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing rabbit SGLT1, application of α-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (αMDG) to the cytoplasmic solution induced an outward current from cytosolic to external membrane surface. The outward current was Na+- and sugar-dependent, and was blocked by phlorizin, a specific inhibitor of SGLT1. The current-voltage relationship saturated at positive membrane voltages (30–50 mV), and approached zero at −150 mV. The half-maximal concentration for αMDG-evoked outward current (K αMDG0.5 ) was 35 mM (at 0 mV). In comparison, K αMDG0.5 for forward sugar transport was 0.15 mM (at 0 mV). K Na0.5 was similar for forward and reverse transport (≈35 mM at 0 mV). Specificity of SGLT1 for reverse transport was: αMDG (1.0) > D-galactose (0.84) > 3-O-methyl-glucose (0.55) > D-glucose (0.38), whereas for forward transport, specificity was: αMDG ≈ D-glucose ≈ D-galactose > 3-O-methyl-glucose. Thus there is an asymmetry in sugar kinetics and specificity between forward and reverse modes. Computer simulations showed that a 6-state kinetic model for SGLT1 can account for Na+/sugar cotransport and its voltage dependence in both the forward and reverse modes at saturating sodium concentrations. Our data indicate that under physiological conditions, the transporter is poised to accumulate sugar efficiently in the enterocyte.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson J., Smirnova I., Kasho V., Verner G., Kaback H.R., Iwata S. 2003. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 301:610–615
Birnir B., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1991. Voltage-clamp studies of the Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. Pfluegers Arch. 418:79–85
Chen X.-Z., Coady M.J., Jackson F., Berteloot A., Lapointe J.-Y. 1995. Thermodynamic determination of the Na+:glucose coupling ratio for the human SGLT1 cotransporter. Biophys. J. 69:2405–2414
Díez-Sampedro A., Wright E.M., Hirayama B.A. 2001. Residue 457 controls sugar binding and transport in the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 276:49188–48194
Eskandari, S., Loo, D.D.F., Wright, E.M. 1999. Functional asymmetry of the sodium/glucose cotransported. FASEB J. Abs. 399
Falk S., Guay A., Chenu C., Patil S.D., Berteloot A. 1998. Reduction of an eight-state mechanism of cotransport to a six-state model using a new computer program. Biophys. J. 74:816–830
Firnges M.A., Lin J.-T., Kinne R.K.-H. 2001. Functional asymmetry of the sodium-D-glucose cotransporter expressed in yeast secretory vesicles. J. Membrane Biol. 179:143–153
Guan L., Kaback H.R. 2004. Binding affinity of lactose permease is not altered by the H+ electrochemical gradient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:12148–12152
Hazama A., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1997. Presteady-state currents of the Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). J. Membrane Biol. 155:175–186
Hediger M.A., Cody M.J., Ikeda T.S., Wright E.M. 1987. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Nature 330:379–381
Hilgemann D.W. 1995. The giant membrane patch. In: Single Channel Recording, 2nd edn, B. Sakmann, E. Neher, editors. pp. 307–327. Plenum, New York
Hirayama B.A., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1997. Cation effects on protein conformation and transport in the Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 272:2110–2115
Hirayama B.A., Lostao M.P., Panayotova-Heiermann M., Loo D.D.F., Turk E., Wright E.M. 1996. Kinetic and specificity differences between the rat, human and rabbit Na+-glucose cotransporters (SGLT-1). Am. J. Physiol. 270:G919–G926
Ikeda T.S., Hwang E.-S., Coady M.J., Hirayama B.A., Hediger M.A., Wright E.M. 1989. Characterization of a Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. J. Membrane Biol. 110:87–95
Kaunitz J.D., Wright E.M. 1984. Kinetics of sodium D-glucose cotransporter in bovine intestinal brush border vesicles. J. Membrane Biol. 79:41–51
Kessler M., Semenza G. 1983. The small-intestinal Na+, D-glucose cotransporter: An asymmetric gated channel (or pore) responsive to Δψ. J. Membrane Biol. 76:27–56
Loo D.D.F., Eskandari S., Hirayama B.A., Wright E.M. 2002. A kinetic model for secondary active transport. In: Membrane Transport and Renal Physiology. The IMA Volumes in Mathematics and its Applications. Vol. 129. H.E. Layton, A.M. Weinstein, editors, pp. 65–83. Springer-Verlag, New York
Loo D.D.F., Hazama A., Supplisson S., Turk E., Wright E.M. 1993. Relaxation kinetics of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5767–5771
Loo D.D.F., Hirayama B.A., Gallardo E., Lam J., Turk E., Wright E.M. 1998. Conformational changes couple Na+ and glucose transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:7789–7794
Mackenzie B., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1998. Relationships between Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) currents and fluxes. J. Membrane Biol. 162:101–106
Meinild A.-K., Hirayama B.A., Wright E.M., Loo D.D.F. 2002. Fluorescence studies of ligand-induced conformational changes of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Biochemistry 41:1250–1258
Panayotova-Heiermann M., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1995. Kinetics of steady state and charge movements associated with the rat Na+/glucose cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 270:27099–27105
Parent L., Supplisson S., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1992a. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: I. Voltage-clamp studies. J. Membrane Biol. 125:49–62
Parent L., Supplisson S., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1992b. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: II. A transport model under nonrapid equilibrium conditions. J. Membrane Biol. 125:63–79
Parent L., Supplisson S., Loo D.D.F., Wright E.M. 1992c. Errata. J. Membrane Biol. 130:203
Press W.H., Flannery B.P., Teukolsky S.A., Vetterling W.T. 1986. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Quick M., Tomasevic J., Wright E.M. 2003. Functional asymmetry of the human Na+/glucose transporter (hSGLT1) in bacterial membrane vesicles. Biochemistry 42:9147–9152
Sauer G.A., Nagel G., Koepsell H., Bamberg E., Hartung K. 2000. Voltage and substrate dependence of the inverse transport mode of the rabbit Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). FEBS Lett. 469:98–100
Segal I.H. 1975. Enzyme kinetics. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Umbach J.A., Coady M.J., Wright E.M. 1990. The intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes is electrogenic. Biophys. J. 57:1217–1224
Wang D., Deken S.L., Whitworth T.L., Quick M.W. 2003. Syntaxin 1A inhibits GABA flux, efflux, and exchange mediated by the rat brain GABA transporter GAT1. Mol. Pharmacol. 64:905–913
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Manuela Contreras for her assistance with the oocytes, and Drs. Andrea Doering and Ken Phillipson for guidance in establishing the giant-patch method. This work was supported by NIH grant DK-19567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eskandari, S., Wright, E. & Loo, D. Kinetics of the Reverse Mode of the Na+/Glucose Cotransporter. J Membrane Biol 204, 23–32 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0743-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0743-x