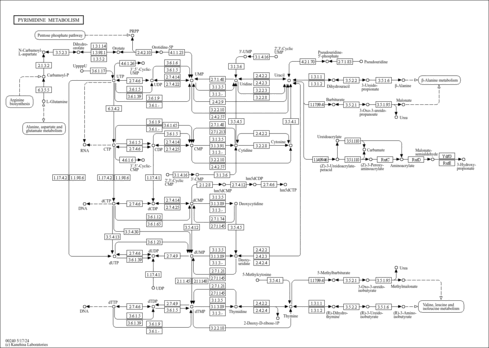
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(N)=O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1584.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1622.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1596.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1673.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1477.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2225.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1570.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1550.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2370.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1660.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1612.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2257.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1738.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1558.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2347.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1664.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1588.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1906.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1716.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1597.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1974.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1730.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1741.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1996.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1765.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1757.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1711.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(N)=O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1836.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1894.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1833.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2120.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1890.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2274.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2030.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1976.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CN(C(N)=O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2477.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2123.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1993.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2327.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2164.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1981.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2351.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2325.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2208.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2243.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2352.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2233.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[C@@H](CNC(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2248.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2384.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2313.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2289.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2599.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2520.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 |
| Ureidoisobutyric acid,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[C@@H](CN(C(=O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2215.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 |