| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 14:17:47 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:14 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002307 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0006507
- HMDB02307
- HMDB06507
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Acrylyl-CoA |
|---|
| Description | Acrylyl-CoA, also known as propenoyl-CoA or acryloyl-CoA, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a coenzyme A substructure linked to an acyl chain. Thus, acrylyl-CoA is considered to be a fatty ester. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on Acrylyl-CoA. |
|---|
| Structure | CC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)C=C InChI=1S/C24H38N7O17P3S/c1-4-15(33)52-8-7-26-14(32)5-6-27-22(36)19(35)24(2,3)10-45-51(42,43)48-50(40,41)44-9-13-18(47-49(37,38)39)17(34)23(46-13)31-12-30-16-20(25)28-11-29-21(16)31/h4,11-13,17-19,23,34-35H,1,5-10H2,2-3H3,(H,26,32)(H,27,36)(H,40,41)(H,42,43)(H2,25,28,29)(H2,37,38,39)/t13-,17-,18-,19+,23-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Acryloyl-coenzyme A | ChEBI | | coenzyme A, S-2-Propenoate | ChEBI | | Propenoyl-CoA | ChEBI | | Acryloyl-CoA | Kegg | | coenzyme A, S-2-Propenoic acid | Generator | | Acryloyl coenzyme A | HMDB | | Acrylyl coenzyme A | HMDB | | Acrylyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | Propenoyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | Acrylyl-CoA | ChEBI |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C24H38N7O17P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 821.58 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 821.12577496 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({hydroxy[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-[(2-{[2-(prop-2-enoylsulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]propoxy]phosphoryl}oxy)phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | acrylyl-coa |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 5776-58-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)C=C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C24H38N7O17P3S/c1-4-15(33)52-8-7-26-14(32)5-6-27-22(36)19(35)24(2,3)10-45-51(42,43)48-50(40,41)44-9-13-18(47-49(37,38)39)17(34)23(46-13)31-12-30-16-20(25)28-11-29-21(16)31/h4,11-13,17-19,23,34-35H,1,5-10H2,2-3H3,(H,26,32)(H,27,36)(H,40,41)(H,42,43)(H2,25,28,29)(H2,37,38,39)/t13-,17-,18-,19+,23-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | POODSGUMUCVRTR-IEXPHMLFSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl coas. These are organic compounds containing a coenzyme A substructure linked to an acyl chain. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Alkyl phosphate
- Imidolactam
- Fatty amide
- Monosaccharide
- Pyrimidine
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Azole
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Acrylic acid or derivatives
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Sulfenyl compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxide
- Organosulfur compound
- Alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA GC-MS (TMS_1_8) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-0000000090-2cb19ca33488da08fcd1 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0fef-9000002530-a4b6c37fc5a00aee084c | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00fr-9001404800-b45b4c03918ee376c5a1 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dr-0300000090-d3c1edf3772f755e2981 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0901100020-fb5ef610714cd38750c6 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Acrylyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-1129000000-1f80bd9b5f4279108e81 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
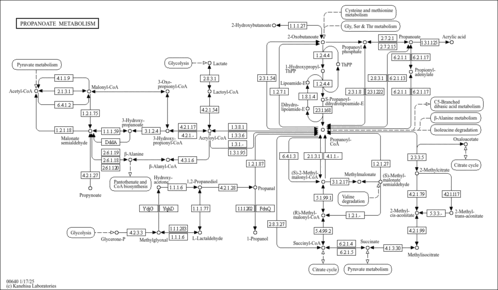
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022958 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 7821999 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00894 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | ACRYLYL-COA |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 446 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 9543026 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15513 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | PRPNCOA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Symes, Kenneth Charles; Collier, Simon Andrew; Armitage, Yvonne Christine; Mistry, Rajesh; Baranyai, Robert. Biocatalytic manufacturing of (meth)acrylic esters. PCT Int. Appl. (2007), 40pp. CODEN: PIXXD2 WO 2007039415 A1 20070412 CAN 146:400675 AN 2007:409912 |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - OMMBID: http://genetics.accessmedicine.com/server-java/Arknoid/amed/mmbid/co_chapters/ch094/ch094_p03.html [Link]
|
|---|