| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2006-08-12 20:14:46 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-10-13 04:41:35 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003405 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | D-Lysine |
|---|
| Description | D-Lysine, also known as D-lysin or DLY, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as d-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the D-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. D-Lysine exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. D-Lysine has been detected, but not quantified in, a few different foods, such as anatidaes (Anatidae), chickens (Gallus gallus), and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa domestica). This could make D-lysine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. D-Lysine is a primary metabolite. Primary metabolites are metabolically or physiologically essential metabolites. They are directly involved in an organism’s growth, development or reproduction. Based on a literature review a significant number of articles have been published on D-Lysine. |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C6H14N2O2/c7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)/t5-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (R)-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid | ChEBI | | D-2,6-Diaminohexanoic acid | ChEBI | | D-Lysin | ChEBI | | DLY | ChEBI | | (R)-2,6-Diaminohexanoate | Generator | | D-2,6-Diaminohexanoate | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H14N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 146.19 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 146.105527699 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | D-lysine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 923-27-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H14N2O2/c7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)/t5-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | KDXKERNSBIXSRK-RXMQYKEDSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as d-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the D-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | D-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - D-alpha-amino acid
- Medium-chain fatty acid
- Amino fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | |
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| D-Lysine,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN | 1465.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O | 1618.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O | 1589.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1579.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1678.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2345.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1618.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1735.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 2354.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1722.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1737.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2247.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1854.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1770.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 2773.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1731.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1705.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 2500.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1715.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1842.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1896.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1783.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1800.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2231.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1823.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1887.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2276.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1915.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 1873.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2136.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1875.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1866.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2048.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1907.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1947.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 1874.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1891.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1955.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1836.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2051.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1993.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2008.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2136.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2055.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1835.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN | 1694.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O | 1876.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O | 1836.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2059.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2069.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2390.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2071.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2136.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2421.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2226.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2125.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2324.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2263.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2173.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2691.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2175.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2105.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2462.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2385.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2384.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2244.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2448.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2371.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2395.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2490.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2462.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](N)CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2452.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2597.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2430.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 2376.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2564.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2419.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2317.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2795.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2656.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2331.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2800.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2646.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCCC[C@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2305.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2889.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2706.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCCC[C@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2377.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3160.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2898.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | D-Lysine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](CCCCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2379.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - D-Lysine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0f8a-2900000000-d5972dfce0860da55a0a | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0f89-9700000000-d8e3259076e214ba9a3f | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a5c-9000000000-0b901a2eb0a82d41fc3d | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-603377bb44b83d433b77 | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-3900000000-e5d6ccb8cd7879780faf | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9100000000-e7f9a18ab48141069fee | 2016-08-03 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-94cae94fd691bdbb4d74 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0900000000-600019f71b72fb289dee | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-bad9cb982e2df334ab55 | 2021-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-9600000000-dcc75a035223a66e7266 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-001i-9000000000-b8581377af4d2519e68c | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - D-Lysine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-9e3d1f9dd58cb0efce55 | 2021-09-23 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm (predicted from logP)
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
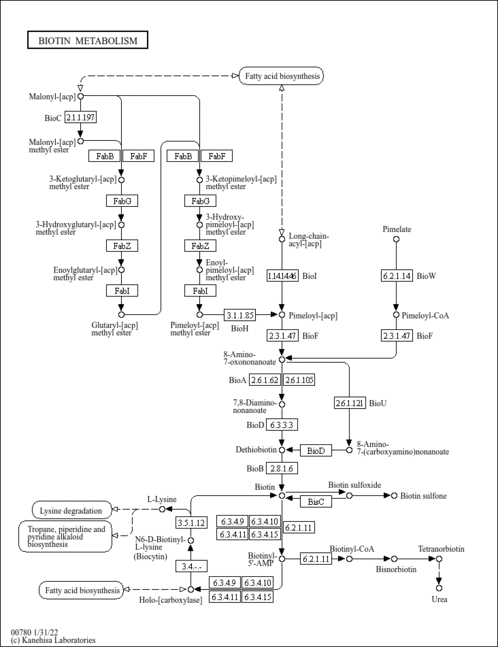
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB03252 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB023163 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 51793 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00739 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-219 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Lysine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 57449 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 16855 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | Not Available |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | rw1107831 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Furui, Masakatsu; Takahashi, Eiji; Seko, Hiroyasu. Process for preparing D-lysine. Eur. Pat. Appl. (1996), 7 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Wakisaka K, Arano Y, Uezono T, Akizawa H, Ono M, Kawai K, Ohomomo Y, Nakayama M, Saji H: A novel radioiodination reagent for protein radiopharmaceuticals with L-lysine as a plasma-stable metabolizable linkage to liberate m-iodohippuric acid after lysosomal proteolysis. J Med Chem. 1997 Aug 1;40(16):2643-52. [PubMed:9258371 ]
- Darling PB, Bross R, Wykes LJ, Ball RO, Pencharz PB: Isotopic enrichment of amino acids in urine following oral infusions of L-[1-(13)C]phenylalanine and L-[1-(13)C]lysine in humans: confounding effect of D-[13C]amino acids. Metabolism. 1999 Jun;48(6):732-7. [PubMed:10381147 ]
- Bross R, Ball RO, Pencharz PB: Development of a minimally invasive protocol for the determination of phenylalanine and lysine kinetics in humans during the fed state. J Nutr. 1998 Nov;128(11):1913-9. [PubMed:9808642 ]
- Hayman MW, Smith KH, Cameron NR, Przyborski SA: Growth of human stem cell-derived neurons on solid three-dimensional polymers. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2005 Mar 31;62(3):231-40. Epub 2004 Dec 30. [PubMed:15733583 ]
|
|---|