Showing metabocard for Hydrogen peroxide (HMDB0003125)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2006-05-22 15:12:34 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2023-02-21 17:16:32 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003125 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Hydrogen peroxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a very pale blue liquid that appears colourless in a dilute solution. H2O2 is slightly more viscous than water and is a weak acid. H2O2 is unstable and slowly decomposes in the presence of light. It has strong oxidizing properties and is, therefore, a powerful bleaching agent that is mostly used for bleaching paper. H2O2 has also found use as a disinfectant and as an oxidizer. H2O2 in the form of carbamide peroxide is widely used for tooth whitening (bleaching), both in professionally- and in self-administered products. H2O2 is a well-documented component of living cells and is a normal metabolite of oxygen in the aerobic metabolism of cells and tissues. A total of 31 human cellular H2O2 generating enzymes has been identified so far (PMID: 25843657 ). H2O2 plays important roles in host defence and oxidative biosynthetic reactions. At high levels (>100 nM) H2O2 is toxic to most cells due to its ability to non-specifically oxidize proteins, membranes and DNA, leading to general cellular damage and dysfunction. However, at low levels (<10 nM), H2O2 functions as a signalling agent, particularly in higher organisms. In plants, H2O2 plays a role in signalling to cause cell shape changes such as stomatal closure and root growth. As a messenger molecule in vertebrates, H2O2 diffuses through cells and tissues to initiate cell shape changes, to drive vascular remodelling, and to activate cell proliferation and recruitment of immune cells. H2O2 also plays a role in redox sensing, signalling, and redox regulation (PMID: 28110218 ). This is normally done through molecular redox “switches” such as thiol-containing proteins. The production and decomposition of H2O2 are tightly regulated (PMID: 17434122 ). In humans, H2O2 can be generated in response to various stimuli, including cytokines and growth factors. H2O2 is degraded by several enzymes including catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD), both of which play important roles in keeping the amount of H2O2 in the body below toxic levels. H2O2 also appears to play a role in vitiligo. Vitiligo is a skin pigment disorder leading to patchy skin colour, especially among dark-skinned individuals. Patients with vitiligo have low catalase levels in their skin, leading to higher levels of H2O2. High levels of H2O2 damage the epidermal melanocytes, leading to a loss of pigment (PMID: 10393521 ). Accumulating evidence suggests that hydrogen peroxide H2O2 plays an important role in cancer development. Experimental data have shown that cancer cells produce high amounts of H2O2. An increase in the cellular levels of H2O2 has been linked to several key alterations in cancer, including DNA changes, cell proliferation, apoptosis resistance, metastasis, angiogenesis and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) activation (PMID: 17150302 , 17335854 , 16677071 , 16607324 , 16514169 ). H2O2 is found in most cells, tissues, and biofluids. H2O2 levels in the urine can be significantly increased with the consumption of coffee and other polyphenolic-containing beverages (wine, tea) (PMID: 12419961 ). In particular, roasted coffee has high levels of 1,2,4-benzenetriol which can, on its own, lead to the production of H2O2. Normal levels of urinary H2O2 in non-coffee drinkers or fasted subjects are between 0.5-3 uM/mM creatinine whereas, for those who drink coffee, the levels are between 3-10 uM/mM creatinine (PMID: 12419961 ). It is thought that H2O2 in urine could act as an antibacterial agent and that H2O2 is involved in the regulation of glomerular function (PMID: 10766414 ). | Read more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| Show more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | H2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 34.0147 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 34.005479308 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | peroxol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | hydrogen peroxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 7722-84-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/H2O2/c1-2/h1-2H | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as homogeneous other non-metal compounds. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds in which the largest atom belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Homogeneous other non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physiological effect | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disposition | Biological location
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Process | Naturally occurring process
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Molecular Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Molecular Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized
| Show more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GC-MS Spectra
MS/MS Spectra
IR Spectra
| Show more...|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biospecimen Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
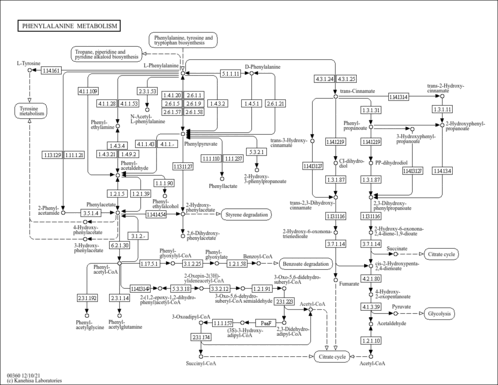
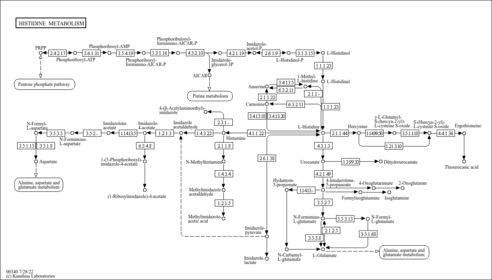
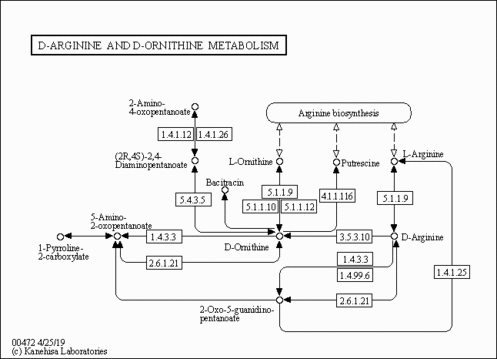
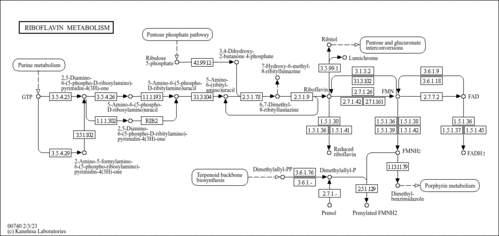
| Pathways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Disorders and Diseases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disease References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated OMIM IDs | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB11091 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB014562 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 763 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | C00027 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | HYDROGEN-PEROXIDE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | 33570 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Hydrogen_peroxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 784 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 16240 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VMH ID | H2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000411 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Good Scents ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| Show more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 53 proteins in total.
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Metabolizes sarcosine, L-pipecolic acid and L-proline.
- Gene Name:
- PIPOX
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9P0Z9
- Molecular weight:
- 44065.515
Reactions
| Sarcosine + Water + Oxygen → Glycine + Formaldehyde + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| L-Pipecolic acid + Oxygen → 2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Amino acid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Flavoenzyme which catalyzes the oxidation of N(1)-acetylspermine to spermidine and is thus involved in the polyamine back-conversion. Can also oxidize N(1)-acetylspermidine to putrescine. Substrate specificity: N(1)-acetylspermine = N(1)-acetylspermidine > N(1),N(12)-diacylspermine >> spermine. Does not oxidize spermidine. Plays an important role in the regulation of polyamine intracellular concentration and has the potential to act as a determinant of cellular sensitivity to the antitumor polyamine analogs.
- Gene Name:
- PAOX
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6QHF9
- Molecular weight:
- 55512.64
Reactions
| N1-Acetylspermine + Oxygen + Water → Spermidine + Acetamidopropanal + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N1-Acetylspermidine + Oxygen + Water → Putrescine + Acetamidopropanal + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N1,N12-Diacetylspermine + Oxygen + Water → N1-Acetylspermidine + 3-Acetamidobutanal + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- AOX1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06278
- Molecular weight:
- 147916.735
Reactions
| An aldehyde + Water + Oxygen → a carboxylate + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Pyridoxal + Oxygen + Water → 4-Pyridoxic acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Gentisic acid + Hydrogen peroxide → Gentisate aldehyde + Oxygen + Water | details |
| Methylmalonic acid + Hydrogen peroxide → (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde + Oxygen + Water | details |
| 1-Methylnicotinamide + Oxygen + Water → N1-Methyl-4-pyridone-3-carboxamide + Hydrogen peroxide + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 5-Hydroxyindoleacetaldehyde + Oxygen + Water → 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Citalopram aldehyde + Water + Oxygen → Citalopram propionic acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 1-Methylnicotinamide + Oxygen + Water → Nudifloramide + Hydrogen peroxide + Hydrogen Ion | details |
- General function:
- Involved in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the desaturation of acyl-CoAs to 2-trans-enoyl-CoAs. Isoform 1 shows highest activity against medium-chain fatty acyl-CoAs and activity decreases with increasing chain length. Isoform 2 is active against a much broader range of substrates and shows activity towards very long-chain acyl-CoAs. Isoform 2 is twice as active as isoform 1 against 16-hydroxy-palmitoyl-CoA and is 25% more active against 1,16-hexadecanodioyl-CoA.
- Gene Name:
- ACOX1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15067
- Molecular weight:
- 70135.205
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + Oxygen → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in D-amino-acid oxidase activity
- Specific function:
- Selectively catalyzes the oxidative deamination of D-aspartate and its N-methylated derivative, N-methyl D-aspartate.
- Gene Name:
- DDO
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99489
- Molecular weight:
- 40992.53
Reactions
| D-Aspartic acid + Water + Oxygen → Oxalacetic acid + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. MAOB preferentially degrades benzylamine and phenylethylamine.
- Gene Name:
- MAOB
- Uniprot ID:
- P27338
- Molecular weight:
- 58762.475
Reactions
| RCH(2)NHR' + Water + Oxygen → RCHO + R'NH(2) + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Tryptamine + Water + Oxygen → Indoleacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Tyramine + Water + Oxygen → 4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Aminoacetone + Water + Oxygen → Pyruvaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Norepinephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxymandelaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Phenylethylamine + Oxygen + Water → Phenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Serotonin + Water + Oxygen → 5-Hydroxyindoleacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Epinephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxymandelaldehyde + Methylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N-Acetylputrescine + Water + Oxygen → N4-Acetylaminobutanal + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Dopamine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 1-Methylhistamine + Water + Oxygen → Methylimidazole acetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 3-Methoxytyramine + Water + Oxygen → Homovanillin + Hydrogen peroxide + Ammonia | details |
| Normetanephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Metanephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde + Hydrogen peroxide + Methylamine | details |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenamine + Oxygen → Quinoline-4,8-diol + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 5-Hydroxykynurenamine + Water + Oxygen → 4,6-Dihydroxyquinoline + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide + Water | details |
| Citalopram + Oxygen + Water → Citalopram aldehyde + Dimethylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N-Desmethylcitalopram + Oxygen + Water → Citalopram aldehyde + Methylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Didemethylcitalopram + Water + Oxygen → Citalopram aldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic and xenobiotic amines and has important functions in the metabolism of neuroactive and vasoactive amines in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. MAOA preferentially oxidizes biogenic amines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), norepinephrine and epinephrine.
- Gene Name:
- MAOA
- Uniprot ID:
- P21397
- Molecular weight:
- 59681.27
Reactions
| RCH(2)NHR' + Water + Oxygen → RCHO + R'NH(2) + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Tryptamine + Water + Oxygen → Indoleacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Tyramine + Water + Oxygen → 4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Aminoacetone + Water + Oxygen → Pyruvaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Norepinephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxymandelaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Phenylethylamine + Oxygen + Water → Phenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Serotonin + Water + Oxygen → 5-Hydroxyindoleacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Epinephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxymandelaldehyde + Methylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N-Acetylputrescine + Water + Oxygen → N4-Acetylaminobutanal + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Dopamine + Water + Oxygen → 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 1-Methylhistamine + Water + Oxygen → Methylimidazole acetaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 3-Methoxytyramine + Water + Oxygen → Homovanillin + Hydrogen peroxide + Ammonia | details |
| Normetanephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Metanephrine + Water + Oxygen → 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde + Hydrogen peroxide + Methylamine | details |
| 3-Hydroxykynurenamine + Oxygen → Quinoline-4,8-diol + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 5-Hydroxykynurenamine + Water + Oxygen → 4,6-Dihydroxyquinoline + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide + Water | details |
| Citalopram + Oxygen + Water → Citalopram aldehyde + Dimethylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| N-Desmethylcitalopram + Oxygen + Water → Citalopram aldehyde + Methylamine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Didemethylcitalopram + Water + Oxygen → Citalopram aldehyde + Ammonia + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Key enzyme in purine degradation. Catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. Contributes to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Has also low oxidase activity towards aldehydes (in vitro).
- Gene Name:
- XDH
- Uniprot ID:
- P47989
- Molecular weight:
- 146422.99
Reactions
| Xanthine + Water + Oxygen → Uric acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Hypoxanthine + Oxygen + Water → Xanthine + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 1-Methylxanthine + Water + Oxygen → 1-Methyluric acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Paraxanthine + Oxygen + Water → 1,7-Dimethyluric acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Theobromine + Water + Oxygen → 3,7-Dimethyluric acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| 7-Methylxanthine + Oxygen + Water → 7-Methyluric acid + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
| Mercaptopurine + Water + Oxygen → 6-Thiourate + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotate with quinone as electron acceptor.
- Gene Name:
- DHODH
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02127
- Molecular weight:
- 42866.93
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors
- Specific function:
- Oxidizes the CoA-esters of 2-methyl-branched fatty acids (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- ACOX3
- Uniprot ID:
- O15254
- Molecular weight:
- 69574.075
Reactions
| Acyl-CoA + Oxygen → trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-CoA + Hydrogen peroxide | details |
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 53 proteins in total.